Unconventional protein and membrane traffic conference 2016
Secretion of the pro-inflammatory cytokines interleukin-1β and its contribution to inflammation and Alzheimer’s disease.
Rivers-Auty J., Lawrence C., and Brough D.
ARUK 2016
Zinc deficient diet accelerates cognitive decline in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease.
Rivers-Auty J., White C., Daniels M.J.D., Beattie J., Gordon M.J., Brough D., and Lawrence C.
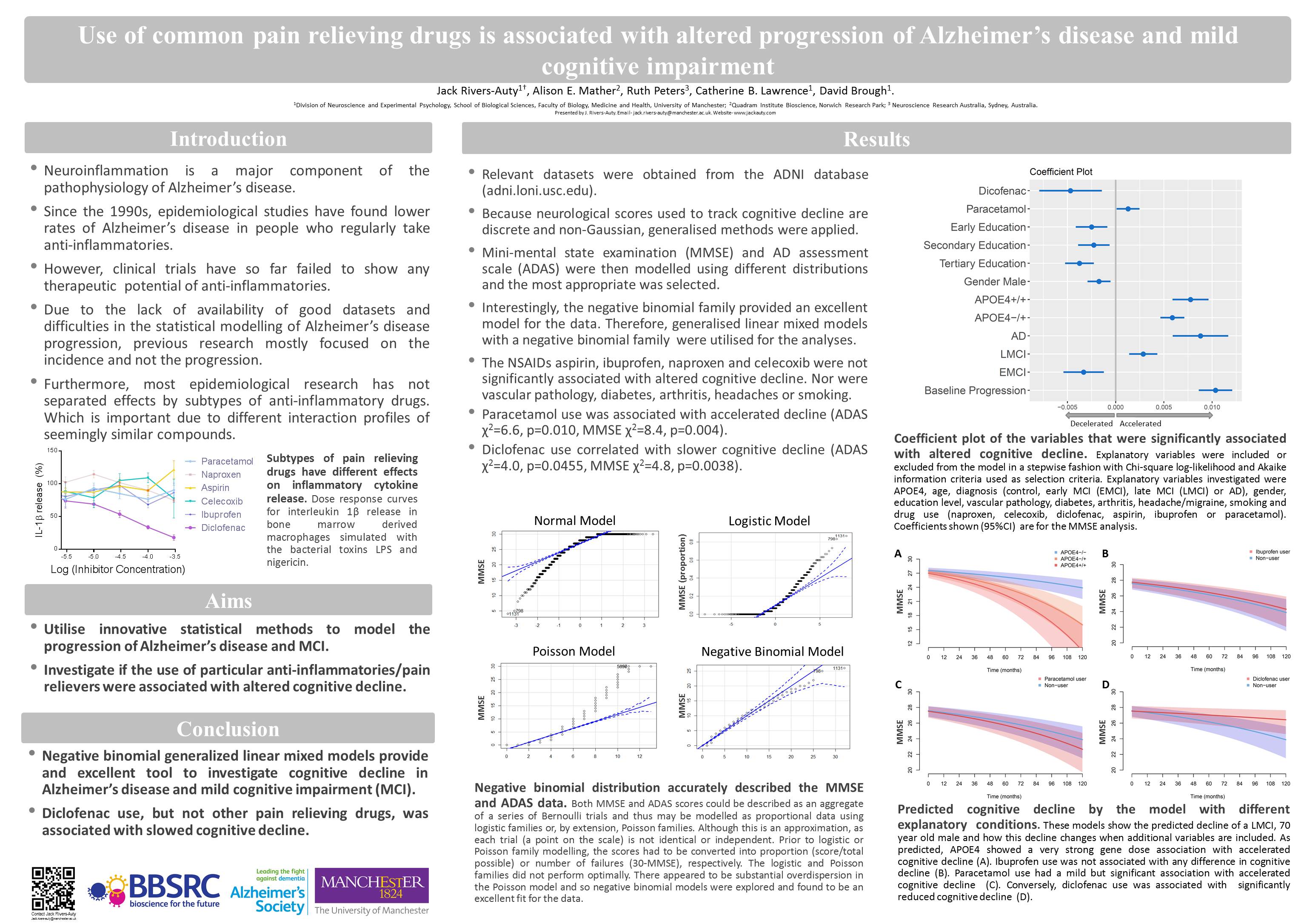
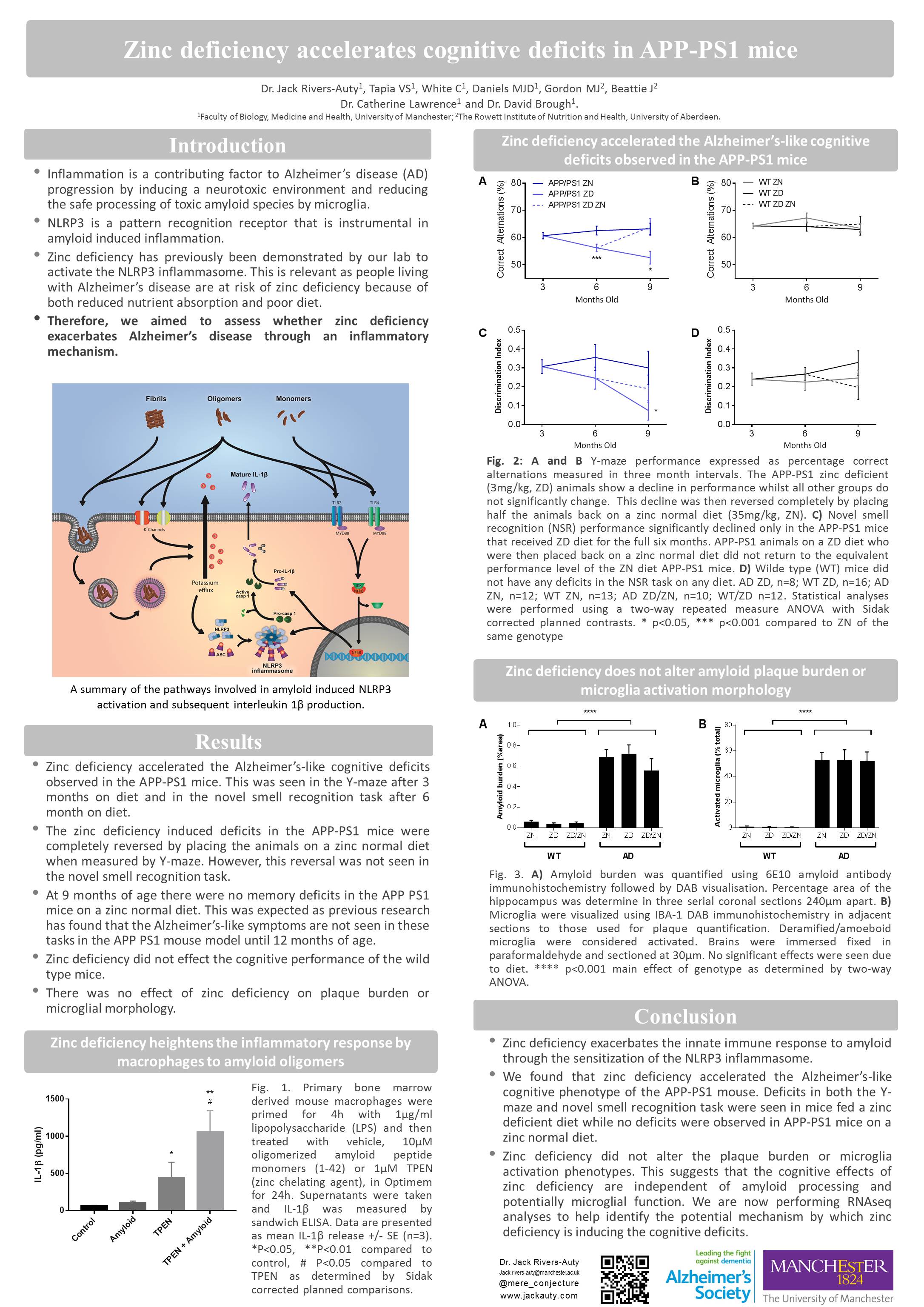
The risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease (AD) increases dramatically as we age. Similarly, the common malnutrition of zinc deficiency is also more prevalent in the elderly more due to changes in diet and zinc absorption as we age. We have shown that zinc deficiency induces the secretion of the inflammatory cytokine interleukin-1β (IL-1β) in macrophages and microglia. This is due to the activation of the IL-1β regulatory protein complex the NLRP3 inflammasome. Neuroinflammation has long been suspected as an exacerbating factor in AD pathology and recently the NLRP3 pattern recognition receptor (PRR) has been found to be the critical in regulated neuroinflammation in mouse models of AD. It is thought that AD associated toxic amyloid oligomers cause disruption in microglia physiology which initiates the formation of the multiprotein NLRP3 inflammasome complex causing the secretion of the IL-1 β. Therefore, this study aimed to assess whether a zinc deficient diet would accelerate the AD behavioural phenotype seen in the APPswe/PS1 mouse model of AD by inducing inflammation through NLRP3 activation. To test this hypothesis, mice were placed on a zinc deficient (3mg/kg) or a zinc normal (35mg/kg) diet for six months. Cognitive/memory performance was evaluated with the Morris water maze, Y-maze and novel smell tasks at baseline, three and six months on diet. To assess if the effect of zinc deficiency was reversible, at the 3 month time-point half the zinc deficient mice were placed back on a zinc normal diet. Our results suggest that zinc deficiency caused memory deficits in the APPswe/PS1 mice at 3 and 6 months on diet while at the same age the wild type mice on a zinc deficient diet and the APPswe/PS1 mice on normal diet showed no deficits. Furthermore, placing the zinc deficient mice on a zinc normal diet partially reverse the memory deficits. Additionally, it was found that innate immune cells from the zinc deficient mice had a hyper-inflammatory phenotype. Therefore, we have shown that zinc deficiency accelerates the AD phenotype in the APPswe/PS1 mice potentially through an inflammatory mechanism. This research aims to further investigate the role of zinc deficiency and NLRP3 in AD using NLRP3-/- mice and novel inhibitors of NLRP3 activation.
ANZLAA 2014
The blind leading the blind. Animal facility staff and researchers working together to reduce bias in animal research.
J.R. Rivers-Auty
In 1799 George Washington became ill with what may have been influenza; three doctors treated him, he was prescribed mercury pills and each doctor drained him of a pint or more of his blood in a procedure called “bloodletting”. He died that night, most likely because of the treatments given rather than the illness itself. The doctors involved believed that their treatments would work based on hundreds of personal observations. This historic case study helps to demonstrate that one of the most important discoveries in human history is that personal observations are one of the least reliable forms of scientific evidence. Or simply, we cannot trust ourselves to unbiasedly observe the effects of an intervention Since George Washington’s tragic end, there have been huge advancements in how we research, particularly the use of randomization and blinding. Yet these crucial methodological steps, which can be complicated, are normally described in journal articles with one simple line “animals were randomly allocated to the treatment groups and all experiments were performed in a blinded manner”, or sometimes not described at all. Meta-analyses of recent animal research have shown that the efficacy of a putative treatment dramatically increases as the number of methodological steps that are blinded decreases. Despite this evidence of bias in animal research, the subject of how, what and when to blind is not often discussed. This presentation aims to address the intricacies of randomization and blinding, and argues that animal facility staff should play an integral role in these important methodological steps. Additionally, greater collaboration between researchers and animal facility staff will produce higher quality research as well as reducing the number of animals that, in the name of science, receive the same level of care as George Washington.
AWCBR 2009
A New Look at an Old Model: Anaylsing Predicting Factors of Infarct Size in a Rat Perinatal Ashpyxia Model
J.R. Rivers, B.A. Sutherland and J.C. Ashton
Hypoxia-ischemia (HI) is popular model of perinatal asphyxia. It involves a unilateral ligation of an internal carotid artery, followed by a period of exposure to 8% oxygen 92% nitrogen. The model has proved to be sufficiently flexible for it to be applied to rats and mice across a range of age groups. The cerebral infarct caused by HI is very similar to that caused by rat stroke models that involve a middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO). Because of this, HI has also been used as a model of thrombolytic and embolic stroke (Northington, 2006). Advantages of the model include its simplicity, the brief period it takes to perform, a low requirement for specialized equipment and a low mortality rate. However, the model is also very highly variable with respect to the degree of cerebral damage induced (Saeed et al., 1993). A notable source of variation is large differences in the morphology of major arterial collateral blood vessels (Brown, 1966). Our study investigates predictive factors of infarct size and the variability of infarction caused by HI on P26 rats. HI was performed on P26 rats. 3 days post HI the rats were sacrificed and their brains sectioned and stained for active mitochondria with triphenyltetrazolium chloride (TTC). Infarct volumes were calculated and compared with factors observed during hypoxia and post HI, including weight change and seizure activity. These data were then used in a statistical model to predict infarct size. As the seizure behaviour during HI was shown to be correlative with infarct size, we proposed that the HI model should use seizure behaviour as the end point of the period of hypoxia, rather than using a set period of time for all animals. The adjusted model gave less variable infarct sizes, lower mortality, and fewer rats with no infarction. Also, the mean infarct size in rats subject to the adjusted model was smaller and more consistently located. Importantly, this smaller infarction is more similar to that observed following human perinatal asphyxia and stroke compared with the conventional model. From this study we have developed a simple, non-invasive way of predicting infarct size in the HI model and developed a variation in the model that produces infarctions in the cerebrum that have greater consistency in size than the original model, more closely model human pathology, and provide greater statistical power for the testing of neuroprotectant treatments.
ASCEPT 2009 (winner of the Fred Fastier Student Speaking Prize)
Effects of the CBII partial agonist GW405833 on neurological damage cause by hypoxia ischemia in rats.
J.R. Rivers and J.C. Ashton.
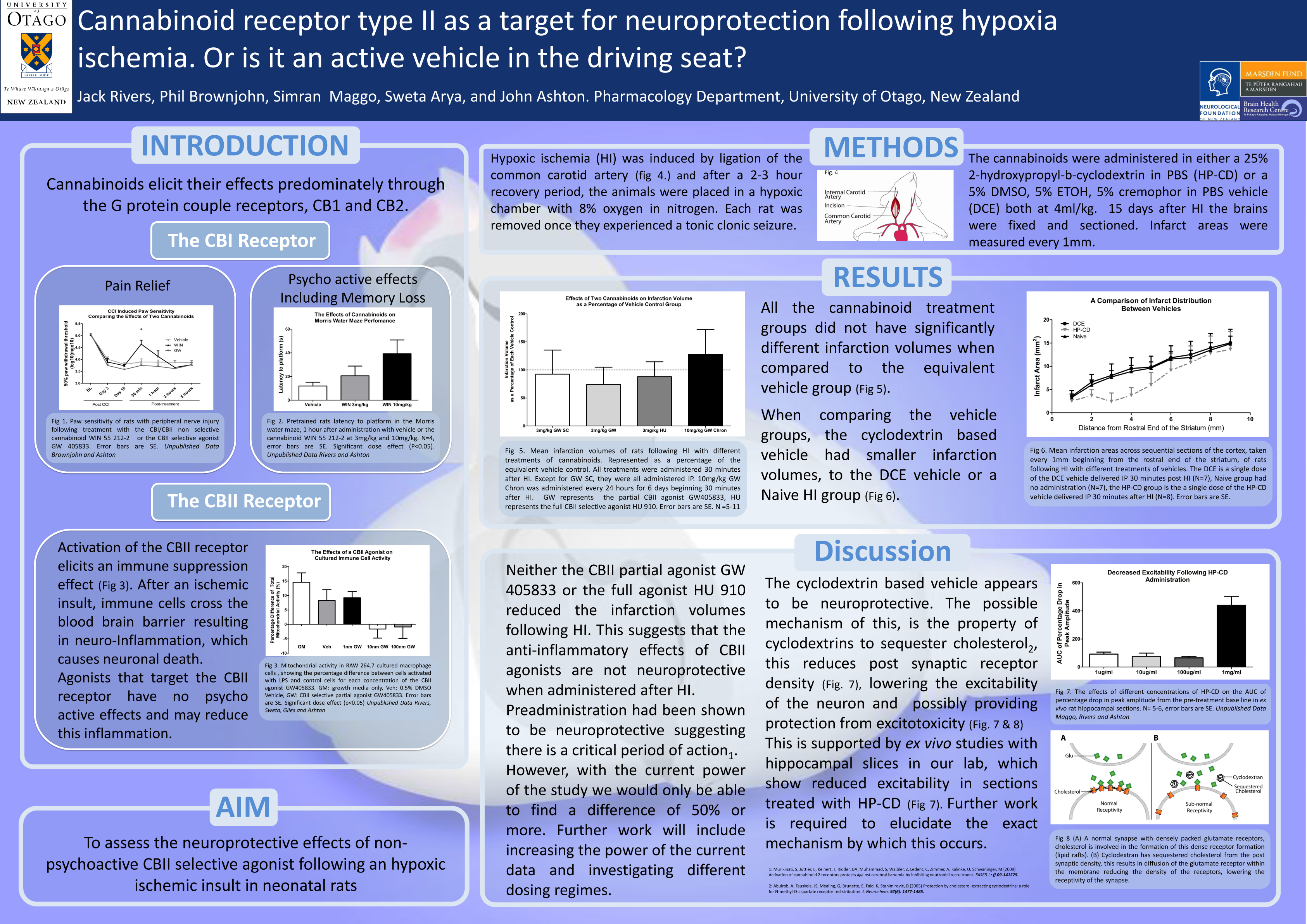
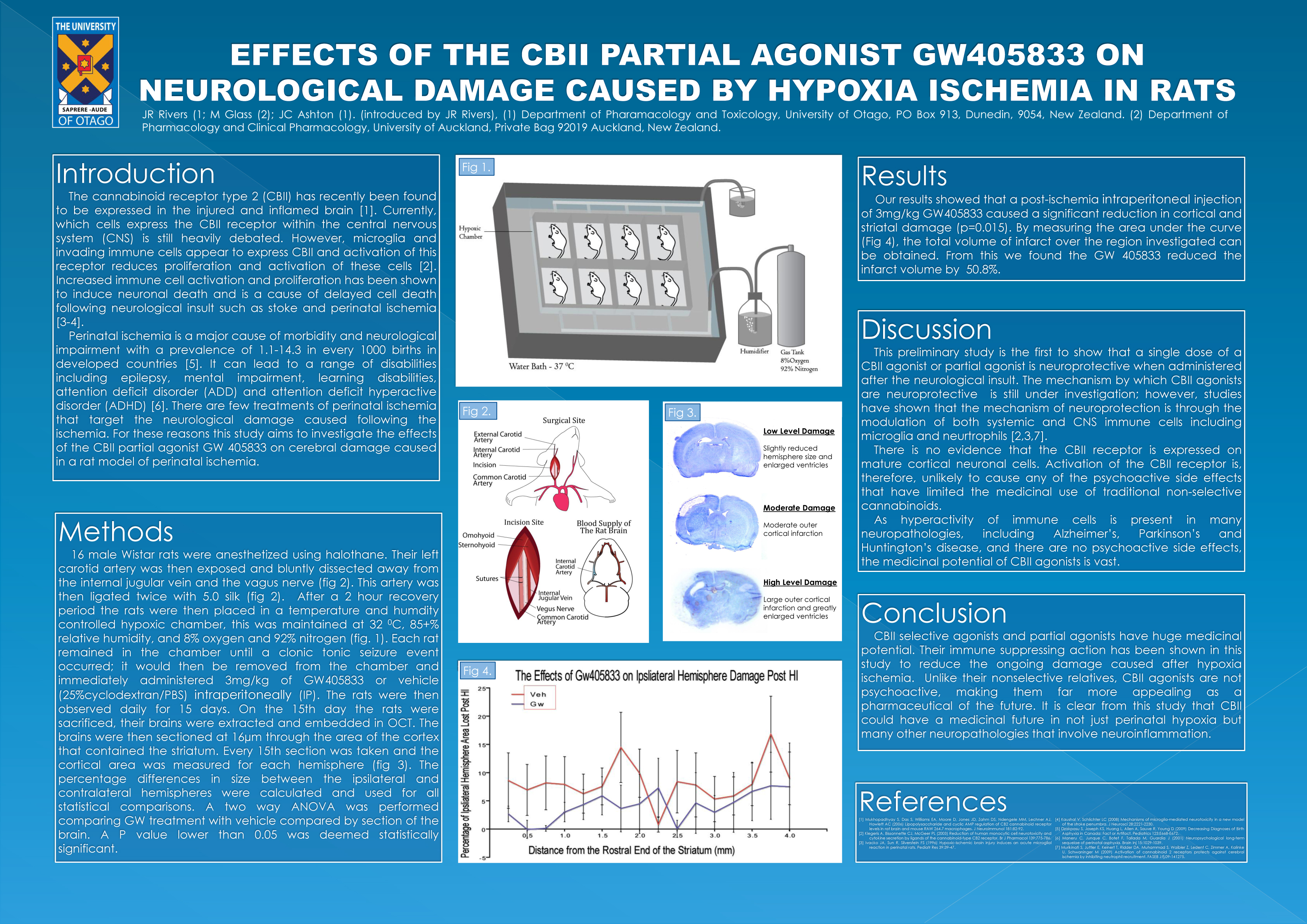
Two described cannabinoids receptors have been found in the human body, cannabinoid receptor type 1 (CBI) found ubiquitously through the central nervous system (CNS), and cannabinoid receptor type 2 (CBII) found primarily in systemic immune cells. Non-selective cannabinoids have been used in the treatment of many conditions including, nausea, loss of appetite, neuropathic pain and inflammatory diseases. Also, cannabinoids had been found in animal studies to be neuroprotective, possibly due to cannabinoids anti-inflammatory properties. The use of cannabinoids as a range of therapeutic drugs was limited by the psycho-active side-effects of non-selective cannabinoids. Recently, the CBII receptor has been found within the CNS. The exact distribution is controversial; however, it appears that activation of the CBII receptor has little or no psycho-active effects. Therefore, recent research has investigated whether specific CBII activation may have the treatment capabilities of non-selective cannabinoids without the unwanted psycho-active side-effects. For this reason the current study investigates whether the CBII selective partial agonist GW405833 provides any neuroprotection in a rat hypoxia ischemia model. Cohorts of 7-8 rats underwent hypoxia ischemia, they were then administered with 3mg/kg of the CBII selective partial agonist GW405833 or vehicle, either subcutaneously or intra-peritoneally. The rats were then sacrificed and assessed for neurological damage with either triphenyltetrazolium chloride (TTC) or cresyl violet staining. Our results show little or no neuroprotection. These results differed greatly from other studies investigating CBII agonist’s neuroprotective qualities. From our study it is clear that the role of CBII in neuroprotection is still unclear and further investigation is required to further assess CBII agonists as potential therapeutic drugs for neurological damage.
ASCEPT 2008 (Second Place in the Fred Fastier Student Speaking Prize)
Preliminary investigations into the specificity of antibody probes raised against the cannabinoid CBII receptor.
JR Rivers; BA Sutherland, PW Browjohn; M Glass; JC Ashton.
The distribution of expression of the cannabinoid CBII receptor is controversial, particularly within the CNS. A recent study has questioned the specificity of a number of CBI antibodies (Grimsey et al., 2008). As studies that aim to investigate the expression levels and patterns of CBII often involve techniques that rely on antibodies for CBII, we investigated the specificity of several commercial and private CBII antibodies using both Western blot and immunohistochemistry. We have previously found evidence that hypoxia-ischaemia (HI) induces expression of CBII in the rat brain (Ashton et al., 2007). We therefore used a rat model of HI to induce CBII expression in the brain, and investigated differences in the detection of CBII with both immunohistochemistry and Western blotting for the different antibodies, and compared with healthy brains. We also used spleen tissue as a positive control, as splenocytes are known to express high levels of CBII. Organotypic hippocampal slice cultures (OHSCs) subject to oxygen/glucose deprivation were previously probed for CBII with several of the antibodies, and results were compared to spleen tissue. We present the results of these investigations, and discuss how antibodies, although designed to detect the same receptor, can show different levels and different localizations. We argue that prior to any investigation using antibodies, the antibody must be fully validated for each application and that using more than one type of antibody is preferable. With respect to the CBII receptor, we argue that lack of specificity of available antibodies may have critically confounded some published results. Finally, we discuss implications of these investigations on our own future investigations into the role of CBII in neuroinflammation.
Grimsey NL et al (2008) J Neurosci Methods 171(1):78-86.
Ashton JC et al (2007) Neurosci Lett. 412(2):114-7.